Introduction

As we move further into the year, we should take stock of the important changes to the SEO world that everybody needs to be aware of if they want to find success in the industry.
Whether your company is fully online or has an online component to it, you want to employ good SEO strategies to stay afloat in increasingly competitive affiliate or ecommerce industries.
No one’s buying what you’re selling if they can’t even find you in the ocean of companies floating through the internet, so getting a viable SEO strategy can be a surefire way to generate traffic, clicks, and sales from your website.
This guide should be your one-stop-shop for some of the most useful SEO tips for beginners and seasoned marketers alike.
Below we’ve gathered nine SEO principles that are broad enough that most SEO marketers should be able to get something out of them, whether it’s contracted SEO work for somebody else, for your own affiliate marketing site, or for your own ecommerce brand.
If you’re relatively new to the SEO field, we’ve even gone as far as to explain what we call an SEO strategy below.
Table of Contents
What Is An SEO Strategy?

In fact, let’s get into what an SEO strategy is right now before we get into the specifics.
Hopefully, you know by now that Search Engine Optimization is simply the process of increasing visitors to a page, and the site as a whole, by planning ahead and altering the backend of your site to ensure that it shows at the top of people’s search results.
As you can see, the definition of SEO focuses more on the end-goals of optimization, but how do you get there?
That’ll be your SEO strategy, also called an approach in some spaces, which are the specific actions you take in both planning and execution to make your SEO dreams a reality.
While they’re usually presented as a list of actions and things to consider, it’s best to cover as many of them as possible.
In SEO, what you do wrong can do more damage to your site than doing everything right, so think of your strategy as plugging holes in the hull of your boat.
Try to cover as many of these as possible and, if you haven’t got the time or the funds right now, take some notes or come back here at a later date to get the rest covered.
How To Craft A Winning SEO Strategy For 2021

So, let’s get into the strategic tips that every aspiring SEO needs to know so that they can create a viable strategy going into 2021 and beyond.
As the world moves further and further into the Information Age, where more people than ever find businesses online, SEO is going to become important to stand out from the crowd.
1. Choosing Your Keywords
If you know anything about SEO, it’s probably that you need to pick your keywords correctly.
This isn’t as simple as finding the highest volume keywords and targeting straight at those.
If only it were that easy! There are a lot of other things to consider and we’re going to cover them all here.
First, know that everything you do with SEO is built upon the foundation of keywords.

Until we transcend beyond the use of keyboards and spoken voice searches, we search the internet through words and we’ll still be doing so for the foreseeable future.
Those searches are your keywords.
If you search for any given term then Google and other search engines try to give you the most relevant result, all catered by an increasingly sophisticated algorithm.
You want that algorithm to be your friend and the best way to do that is to play ball. This means going after keywords where you can, sure, but it also means choosing your battles.
You can’t rank for every keyword and you shouldn’t spend too much time and energy on a keyword that you can’t realistically achieve.
Think about it, in the time it’ll take to crack a hard keyword, you can target three easier ones and get the same traffic cumulatively.
When thinking about keyword competitiveness, you need to think about specificity.
One-word searches are the vaguest, let’s use the word “shoe” as an example.
When you throw that at the algorithm, you’ll get some basic definitions and then a cavalcade of massive corporations that sell them.
Only these big players rank because “shoe” is very, very competitive and the algorithm finds millions of search results in mere seconds.
By adding more words to your search, you can decrease the search results and in doing so, find keywords that aren’t as competitive.
“Shoe” is a bloodbath but “best shoes for standing all day” is easier to rank for.
These are what we call long-tail keywords and, if you want to get the best rewards for less effort, you should focus on targeting them.
Shoes in general are pretty competitive but just by adding those words, we’ve taken the search results from billions to millions and there are even sites on the front page with a Moz DA rank as low as 30.
Targeting these specific needs also increases the chance that you’ll make sales since these are people who know exactly what you’re looking for.
If you’re an SEO who likes to think about alternative search methods and future-proofing, you’ll also like that long-tail keywords tend to be great for voice search, which is only going to become more important in the future.
2. Analyze Your Competitor’s SEO Strategies

Since business competition started being a thing, savvy entrepreneurs and marketers have analyzed the competition to see what they were doing right and wrong.
Back then, it might have meant donning a trench coat and loitering outside the business or sending an employee or a trusted friend to go through their sale process to see what’s different.
Thanks to the internet, you don’t need to do that anymore.
Analyzing competitors has become easier than ever.
So, you’re getting trampled on a keyword by a competitor who, on paper, you should be able to take on, then what are they doing? Take stock of what they’re doing right and wrong.
Finding out what they’re doing right can reveal flaws in your own strategy by comparison, which allows you to improve.
If they’ve stumbled across a secret to success then there’s no shame in imitating what they do to get ahead.
There are limits to this, of course. Try to avoid one-to-one copies of certain site material that you suspect may be legally protected.
Along with what they’re doing right, find out what they’re doing wrong.
For all you know, your biggest competitors stumbled across great SEO techniques by looking at you and seeing what you weren’t doing.
There’s no reason you can’t do the same to them. Go through their site and see what’s up. Try the following:
- View their site pages and layouts.
- As you do, check out the links and how they’re arranged.
- Read the content on their posts, especially informational ones.
- If financially viable, pass through their sales funnel and compare it with yours.
- Take screenshots along the way to make comparison easier.
So far, we’ve assumed that you even know who your competitors are, which isn’t a ensure.
Simply search the keywords that you’re targeting and look at the first page results that come up.
It’s great to use a tool that shows the domain authority of the sites like MozBar or Ahrefs’ Website Authority Checker. Sites that are around the same DA/DR as yours are usually your beatable competitors.
Backlinks are also important. Ahrefs has a backlink checker that you can use for free, at which point you find the site’s page that challenges the same keyword as you and put it through the tool.
Check out the referring domains and go through the list to identify links they have that you can also get.
Contacting webmasters for link building is its own skill that we’ve discussed further below.
It can come in handy to grab the same links that your competitors have, leveling out the playing field.
3. Create Better or Different Content
If you read your competitor’s content and find that it’s of better quality than yours, you may have a problem.
While there are countless metrics that go into the backend of your site, the simplest way to be better than your competitors is to just be better. This means that your site needs to have good content.
Sometimes this means you need to do what you’ve been doing all along, but better.

Good spelling and grammar are paramount for this and can be challenging if outsourcing your content, so maybe try higher content standards.
Maybe layout is a problem too, which can be where competitor analysis pays off as there are many SEO-friendly site templates available online.
You might be targeting the wrong audiences too, at which point you may need to re-aim your content to the right audiences or change that content entirely to be what your audience desires.
Alternate content forms have taken precedence over the last decade, so check out audio or audio-visual content if nobody’s sticking around to read your written work.
Making your content longer can improve the page’s performance too. Pages with longer content text tend to get more backlinks than the shorter alternatives.
See if you can’t plan your content to be longer than usual, like between 3,000 to 5,000 words.
If you can’t do as many words because of how time-consuming this can be then we’d advise you to focus on shorter-form content that targets user intent where shorter attention spans can get more value, all from less work on your part.
There’s a neat hack that you can use to create a lot of 2,000+ word content pages, however.
Take a look at your existing pages that have over 1,000 words in their main text and make a list of them, then check each to see if there’s nothing you can add.
Can you stick an FAQ section at the bottom? If so, that can add a few hundred words.
Add to these pages until there are 2,000+ words, paying special attention to popular pages that already bring in audiences and have a strong authority profile.
Update content that makes sense to update too. If the content is in the SEO field, then it’s not unusual for pages to be updated regularly due to the ever-changing nature of our industry.
4. Make Your Content Stand Out

Along the same lines, maybe the problem isn’t with the content itself but how that content is presented. You want your content to be organized, logical, and easy to find. HubSpot recommends organizing content into what they call topic clusters.
This is a way of restructuring your site to have your most important pages, called pillar pages, are front and center, which is something that’s perfect for ecommerce websites.
Around these and linked to these pillar pages are cluster pages which go into more detail about topics covered on those pillar pages.
Doing this easier satisfies readership user intent and splits topics into several pages, opening up the possibility of cluster pages themselves ranking on SERPs.
Once you have the site structure working, you need to make sure the content also looks great on-page.
We’ve all seen those ancient sites that were established in the 90s and left to rust, where there’s boring text against a white or grey background and nothing more.
You can’t get away with that nowadays, those sites are often abandoned for a reason because anybody in their right mind who owns a site in 2021 makes their site pleasing to the eye.
A wall of text can be intimidating too, so try to avoid having just word content on each page.
Break that content into bullet points, which also tend to perform better when they’re numbered, so that information is easier to consume.
Also, if visitors are searching for specific info, they can scroll till a heading catches their attention so that they spend more time on the page.
A fractured wall of text is still a wall of text, however, so you should also break it up even more by using images, bullet points, tables, graphs, and charts to make your pages much more palatable.
If you’re explaining complex or niche-specific information, you’ll also want to use screenshots or diagrams so your audience, and even you, can better understand the subject matter.
If you aren’t in a specific niche then pictures can be added for flavor.
You can add images and aesthetic designs to the head of your pages too.
These banners on your blog posts don’t have as practical a purpose as the diagrams but, if a reader clicks off your site because it doesn’t look good, then they don’t get to the good stuff in the first place.
5. Optimize For On-Page SEO
SEO isn’t just what you do on the backend of your website, you also need to pay specific attention to on-page SEO.
Getting people to your site is all well and good but once they’re there, you want them to spend time on your page to increase the chances that they’ll buy something or sign up to any subscriptions or email lists that you’re offering.

On-page SEO is its own entire school of SEO practices that we can’t cover at this point alone, so here’s a brief point by point rundown of what you want to have:
- Internal links from high-authority web pages anchored in keyword text.
- Optimized title tags and meta descriptions.
- SEO-friendly content that keeps them reading.
- Trimmed, neat URLs that are easy to find.
So, what do these mean? It’s relatively simple. We’re talking about link-building next but what you need to know for on-page SEO is that your internal links work best when it’s a high authority site that’s being linked.
This is common knowledge for SEOs, more authority can only be a good thing, but the trick is that the links work best when linking from a high authority page to a low authority page.
This is a great way of giving new pages on your site a little boost.
To ensure that search algorithms understand your pages, you want your title tags and meta descriptions to be fully optimized.
This means incorporating modifying language that the algorithm shows some love to, “best” is a tried and true example, along with informative words like “review” and “guide.”
Sometimes it’s difficult to balance commercially attractive writing with SEO algorithm favorability, which is where part of the skill of copywriting comes into play.
If repeating the same keywords ad nauseam might harm your content, simply use semantic SEO.
This is where you use synonyms and other interrelated jargon around your keyword so that you target the same corners of the internet.
Short URLs tend to win out over long URLs. There are many reasons this may be the case, from them being easier to type manually to ranking higher on SERPs.
They are easier to share too. We’ve all received a link from a friend and hesitated because it’s a wall of numbers and symbols, which isn’t a problem when your URL simply reads “www.example.com/SEO-guide” or something else that’s understandable at a glance.
6. Optimize For Search Intent

As we move into the 2020s and beyond, we’re all expecting to see Google and other search engine providers pushing more towards user search intent.
This is something that was seen in 2019’s BERT Update and the following May 2020 Core Update, where an increased focus on on-site authority over flat keyword quantity and other superficial features turned many people’s SERPs upside-down.
This focus on authority and information-based content came from efforts to figure out what a user wants when they use the search engine, to put the correct pages in front of them.
When SEOs talk about search intent, they mean the reason why somebody is searching online in the first place.
That’s quite a broad definition, as you can imagine, but search intent can be broken down into four different types:
- Informational Intent
- Navigational Intent
- Transactional Intent
- Commercial Investigation
When we see the words “search intent” it’s probably informational intent that we think of first.
This is simply where people online want information about different topics, whether they’re specific or broad.
These people search for everything and anything.
They represent a wide swathe of casual internet users, hence why sites oriented towards affiliate commerce or ecommerce will still make sure they have informational sections of their websites.
As Google moves away from specific search terms and more into user intent, we’ve seen videos and other visual media come up in search instead of written content, making certain niches harder to tackle.
Navigational intent is simply where the users know which site they want to visit and then go there.
When you’ve ever entered your favorite social media site into a search bar, you’ve engaged in navigational search intent.
As you can imagine, it isn’t that useful ranking for navigational search terms unless you’re the one they’re looking for.
These people have their minds set on what they want, so they’re far less likely to stray from that path if your unrelated site pops up in their SERP.
With that said, if they’re looking up your site and it isn’t at the top, or at least on the top half of the first page, then we have a problem.
People should be able to find your site easily when they know it’s your site they want to go to.
That should be one of the easiest searches that web netizens can perform, so something might be wrong with your site’s backend if it isn’t showing up.
Transactional intent and commercial intent are similar but slightly different.
Transactional intent is where somebody searches to find a product or service and, once they find it, it’s highly likely they’ll end up buying something.
Commercial investigation intent, on the other hand, is more the research that may go into an eventual transactional intent search.
Before you make the all-important transactional search for some new hiking boots, you might search beforehand on hiking boots and your local environment to see which types of boots are compatible.
If it’s about a product or service but has a question mark on the end, the search is probably commercial and not transactional yet.
The keywords used are still important, so checking out the main words in a search phrase can help you determine when a search is informational and transactional.
You know this already, even if you’ve never given it much thought.
For example, most of us would assume that somebody searching for terms like “deal” or “buy” are closer to buying than someone looking up words like “information” and “why.”
As for what you can do, you should ensure your landing page gels well with the search intent of your general audience.
If you’re an affiliate site that offers both product/service recommendations alongside informational content, that should be crystal clear.
Similarly, the landing pages of ecommerce sites are especially important for communicating what your site is about and what they can buy there.
Don’t take too much time, if they want to buy then just show them where the goods are.
There’s no need to take any wild stabs in the dark when figuring out search intent if you have an active audience.
That’s because you can ask them in the form of a survey or community post if you have a social media following.
From there, you can get a feel for the general consensus of search activity amongst your audience, allowing you to maximize your site’s search intent success.
7. Implement Link Building Strategies
We’ve mentioned link building several times already, so it’s high time we go into more detail about what you should focus on in regard to link building in 2021.
To do this, let’s go through three distinct link-building strategies that are doing quite well right now in the SEO world.
- Competitor Analysis
- Broken Link Building
- Evangelist Method

Competitor analysis is the oldest school method any SEO can employ when link building. The reason why it’s still used is that it still works.
When targeting keywords that you’re trying to rank for, check out the first SERP that Google throws back at you.
From here, identify any competitors. If that sounds familiar, it’s because competitor analysis is essentially what we described for analyzing competitor’s SEO strategies and finding the referring domains they use, so check back with that section for the full rundown.
As for the others, broken link building is where you go scouting for links on somebody else’s site that may be, well, broken.
This is where the content on the other side is no longer available, rendering the link useless to the site owner.
From there, you can send an email to the webmaster and try to get that link to direct to you instead.
Of course, it needs to be relevant and add value so that your offer gets accepted, and you should be specific by linking to them the exact page you think they should link.
The evangelist method is all about quantity, getting your site’s pages in front of as many people as possible to increase the chances that a site owner sees it.
If they like it, they may reach out with a request to link to you, but usually, you’ll be the one doing the outreach.
Everyone has their own distinct strategies to talk about links and successfully convince somebody to give you them.
A common thread with all link-building advice is that it helps to come across as helpful and relevant, instead of making it obvious you’re just after a hyperlink
8. Track Results

When you’re an SEO, you spend a substantial amount of time looking at metrics, charts, and graphs.
When negotiating with a fickle algorithm like the one that Google keeps around, it’s very important to double back and see what effect your strategies have had.
This is harder than it sounds because you can make a dozen changes to a website, and an individual webpage, at once.
In those cases, which change was it that has contributed to your recent success?
The nature of your site will vary widely from others reading this, so we can’t jump into the backend of your site with you and figure out what you’re doing or not doing right. Instead, check out these ten metrics that you should be following.
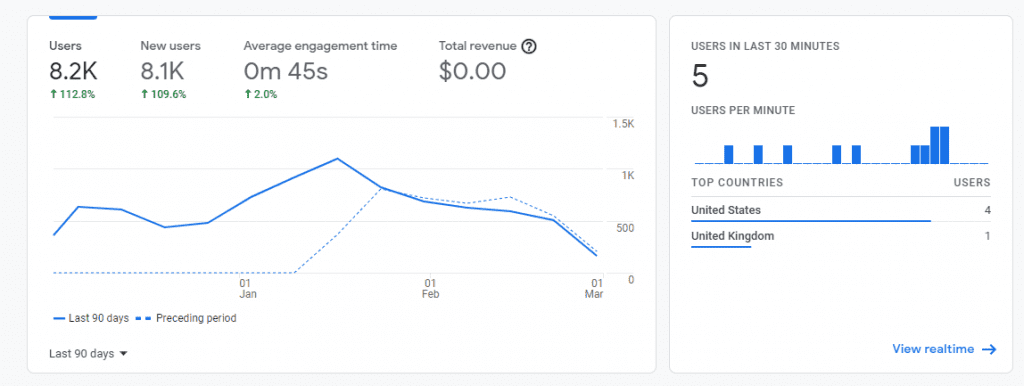
Traffic
Organic traffic in particular, that comes from organic search results that are made by real people.
This is often the metric that any site, no matter what that site offers, gauges its search performance by.
After all, if your site isn’t being served in front of people then you’re going to have trouble getting what you want out of this site.
We’d strongly recommend using Google Analytics if you’re not already. If you’re trying to rank on the most popular search engine in the world, why not use their homegrown analysis program to check out how your website is performing?
Go to the overview report in the audience section, find “add segment” and go to “organic traffic.” There you’ll see the traffic figures, which you should check in with periodically.
Along with organic traffic, you may want to look at branded traffic too.
If you’re building a brand that requires brand awareness on the internet, you can specifically see how many people found your site by searching for your brand name.
This is as easy as adding your brand name (or names) to Google Search Console’s keyword filter and keeping an eye on how many people look up your brand name over time.
Search Rankings
This is directly correlated with organic traffic, of course, since more people will click on the highest-ranking sites that show up on their SERPs.
If SEO could be boiled down to a single sentence, it’s to tailor a site so that it ranks higher in people’s searches.
Higher search rankings equal more traffic, more generated leads, and more successful conversions for your online business.
You want to rank for the correct keywords too. Ranking for the wrong keywords isn’t what you want, even if it is a little impressive that anybody could rank highly for a keyword they’re not even targeting nowadays.
Use tools like Ahrefs and Serpstat. They’re easy to use, just enter our domain name and find your organic SERP results.
You can throw keywords into these sites that you want to track, allowing you to build a suite of keywords you can easily keep an eye on.
You can do the same for your competitors’ websites too if you have a rival site that you’re looking to overtake.
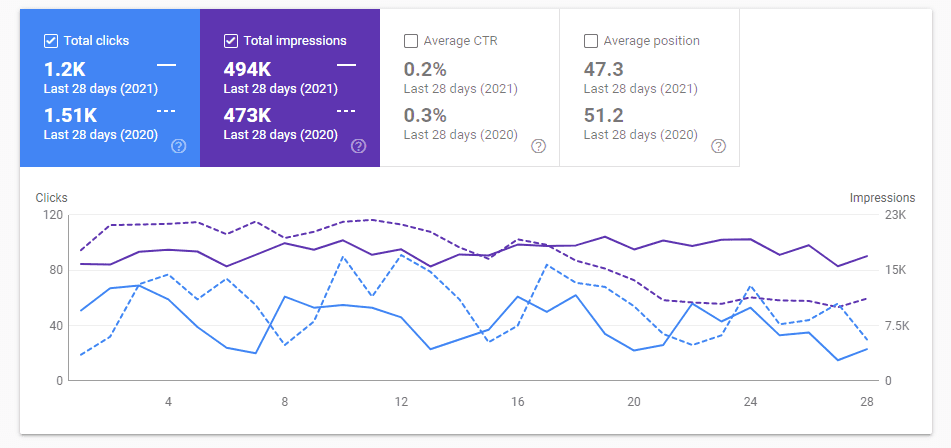
Search Visibility
Connected with search ranking, search visibility is how often your site ranks for the keywords that you actually target.
You can find this in Google’s Search Console, on the performances report page in particular.
The total impressions score is what a lot of you will want to pay attention to.
Each individual impression is a recorded instance of somebody bringing up a page that has your URL somewhere on it. Search visibility is especially important when your site is starting up.
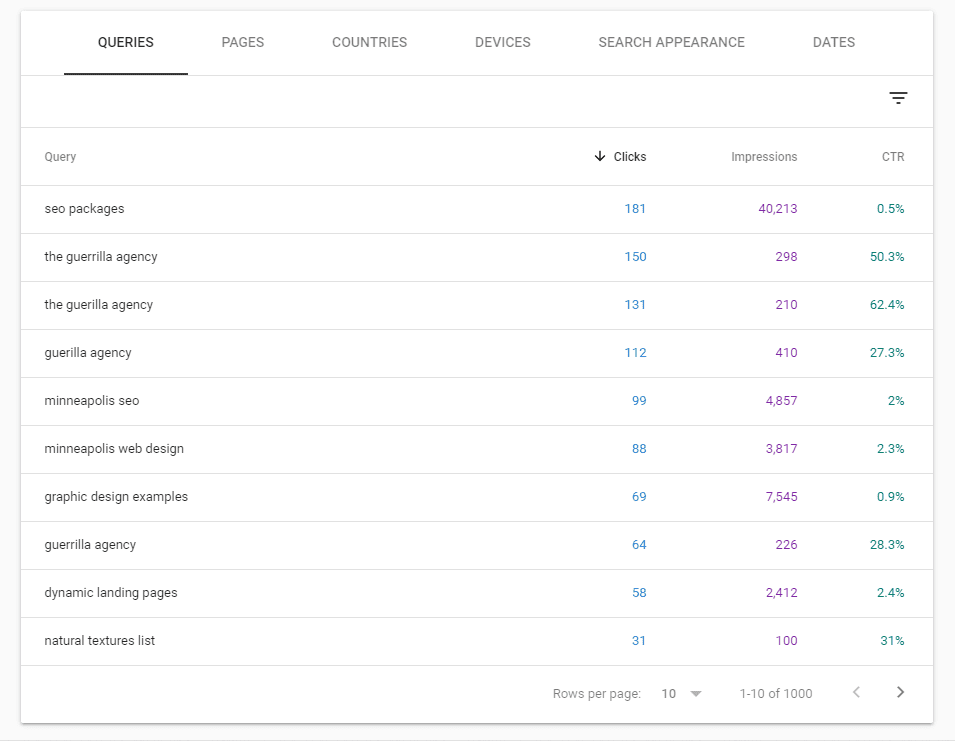
Organic Click-Through Rate
Click-through rate, or CTR, is the performance metric that measures how many people click on your URL when it does show up on their results page.
The law of averages dictates high traffic will lead to a higher CTR, but professional SEOs also focus on maximizing how many clicks they can get from their audience base.
A poor CTR when you have good traffic can indicate a problem with the search snippets that show up on people’s SERPs.
In a line, your site doesn’t look appealing enough at a glance.
This has an effect on future ranking performance as the algorithm will notice that your URL isn’t getting clicked on as many times as the others on that SERP, pushing you down further, so a low CTR is something everybody should be wary of.
CTR can get overlooked, especially if you’re already tracking traffic and SERP rankings, so get back into your Google Search Console and check what your website’s CTR currently is to connect the dots between traffic and ranking results.
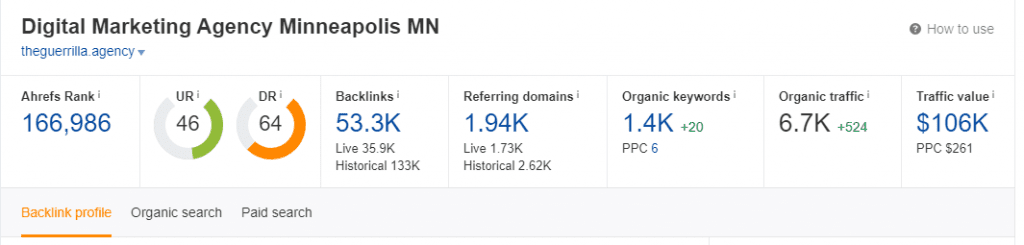
Links
Links, backlinks, in particular, are one of the more important SEO metrics now that Google is looking for authority in its highest ranking search results.
That’s why acquiring backlinks for your site is necessary for SEO success.
You don’t just want a lot of links though; they need to be good links. Low-quality links will do more damage to your webpage’s SEO profile than not having any at all.
You can avoid the bad links by checking the quality of every link you think of adding to your site.
This can be done through backlinks analysis tools like Ahrefs, Majestic, or Moz’s Links Explorer.
No matter which one of the above you choose, you’ll find a link authority index where the links towards the top have a higher authority ranking.
Type in your domain and you should see an informed estimate of your website’s link profile quality.
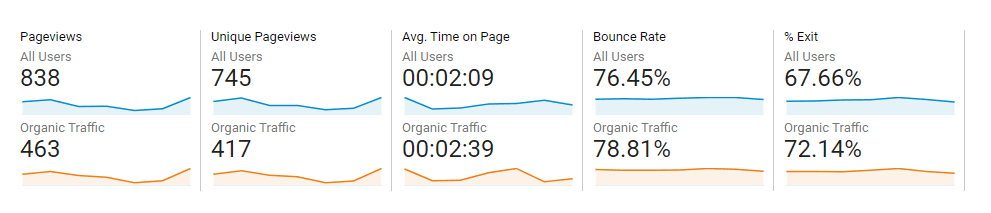
Bounce Rate
This is another of those metrics that the algorithm notices and will use to penalize your site if it gets too high, so pay attention to it.
The bounce rate is the metric that describes how many visitors came to your site and left without taking any recordable actions.
Yes, that means without clicking through one of your links or not buying anything.
That’s bad for business anyway but, as we said, this can harm SEO performance if you let a bad bounce rate fester.
The typical bounce rate can be anywhere from 60% to 80% as netizens tend to have shorter attention spans anyway, so anything above a 80% from organic traffic is a cause for concern and should be addressed.
Google Analytics’ overview report should show you the bounce rate. If it is too high, maybe the page is coming up in unrelated searches and is failing to satisfy users’ search intent.
9. Improve And Update Your Content
Following on from the last point, you should continue to improve and update the content that you’re producing.
That’s right, this is a tactic we’ve mentioned in passing already but it’s important to emphasize that your content doesn’t exist in stasis.
Once you put some content out there, one of the worst things you can do is let it grow stagnant and forget about it.

Before you try mashing the republish button on your site, it’s important that we go through the specific ways you can improve older content and make it more suitable for a 2021 SEO landscape.
Try to refrain from just reposting old content and labeling it as new, or just changing the date in the backend of your website.
Instead, take a look at the article in question and find any images, especially screenshots with identifying information about the date and time they were taken.
Remove and replace them as needed so that your content is justified in being republished since there’ll be new image content there now.
Similarly, delete anything that doesn’t hold up anymore. SEO itself is a great example of this, and it’s something we have personal experience with.
The SEO industry changes a lot from year to year so informational pieces about the latest SEO lifehacks may have a short shelf life.
If possible, replace these defunct strategies with newer, trendier ones that actually work at the moment.
The trendy word count averages that certain SEOs and webmasters use for their site’s content tend to change too.
Right now, marketers are liking slightly longer review content but, at the same time, that Google May 2020 Core Update has seen shorter, more informational content comes out at the top of informational SERPs.
The point being, if your site is old school enough that it has much shorter content than is the norm, then adding more words and republishing these pages is a great and relatively labor-effective way of bringing new interest to your website.
With all of the above in mind, you should just remember that old content can become new content with some elbow grease.
Evergreen content is still better, of course, and you should still be supplying that to your website.
Newer content works much better with the algorithm and is a surefire way to put your site on the very, very large map that is the internet when your site is starting out.
The allure of content republishing is that, by taking older content and repurposing it, you or your commissioned writers can do less work but reap a lot of rewards if that piece of content happens to be a hit with the crowd.
Whether it’s traffic, subscriptions or shares, or even a bump in commercial performance, it all feels even better when you know that you achieved that boost by spending less time and money than you usually do on new content.
Summary

Those have been our nine main tips to craft a winning SEO strategy for 2021.
It’s almost ensured that there’s more knowledge floating around out there, which we’ll probably cover later in the year, but this is everything that you need to know when entering the field right now.
SEO management can often feel like you’re spinning a lot of plates at once, so make sure you have the above properly covered before you try moving onto other SEO improvements.
Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to meet them all immediately, too.
Tuning your website into the perfect SEO machine tends to be an iterative process that is best tackled point by point, so keep this page around and refer back from time to time when you need some inspiration.




